Why Is The System Idle Process Hogging All The Resources?
From the “you can’t make this stuff up department,” this 2003 gem from blogging O.G. John Dvorak:
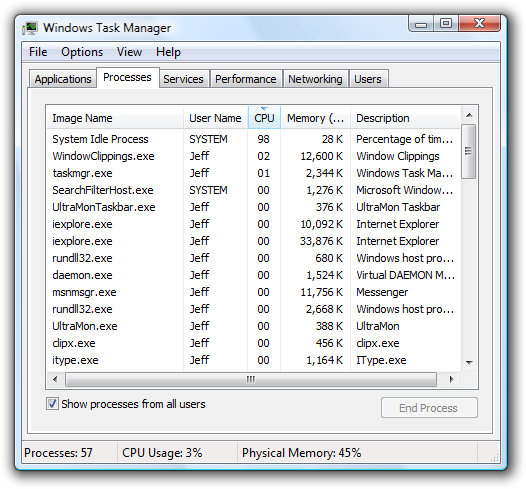
IDLE-TIME PROCESS. Once in a while the system will go into an idle mode, requiring from five minutes to half an hour to unwind. It’s weird, and I almost always have to reboot. When I hit Ctrl-Alt-Delete, I see that the System Idle Process is hogging all the resources and chewing up 95 percent of the processor’s cycles. Doing what? Doing nothing? Once in a while, after you’ve clicked all over the screen trying to get the system to do something other than idle, all your clicks suddenly ignite and the screen goes crazy with activity. This is not right.
I remember reading Dvorak’s PC Magazine column at the time and doing a double-take. Dvoraksayswhat?
In John’s defense, it sounds like he was having some kind of strange, unrelated problem which he wrongly attributed to the idle task. But his profound misunderstanding of how this fundamental bit of computer science works is a wee bit disturbing for a computer journalist of his tenure and stature.
In case there’s anyone reading this who doesn’t understand how the System Idle Process works (Hi Mr. Dvorak!), the Wikipedia entry for Idle task is unusually succinct, so I’ll just quote it in its entirety:
In computing, an idle task is a special task loaded by the OS scheduler only when there is nothing for the computer to do. The idle task can be hard-coded into the scheduler, or it can be implemented as a separate task with the lowest possible priority. An advantage of the latter approach is that programs monitoring the system status can see the idle task along with all other tasks; an example is Windows NT’s System idle process.
On modern processors, where a HLT (halt) instruction saves significant amounts of power and heat, the idle task almost always consists of a loop which repeatedly executes HLT instructions. However, on older computers, where temperature dissipation was almost constant with CPU load, the program would often do useless things, like blink the front panel lights in an amusing or recognizable pattern.
Often, this had the effect on timeshared systems that if one was lucky enough to have access to the computer room, one could glance at the front panel lights to see how busy the machine was. If the idle pattern very rarely showed up, the machine was heavily loaded, and one might go for lunch before waiting for a job to finish; on the other hand, if it was clearly blinking the idle pattern, one might run the job immediately.
In Unix-like operating systems such as Linux, the idle task has process ID zero, and never exits. Another specially distinguished task on Unix-like operating systems is the init process, which does little more than wait around for its child processes to die.
In other words, if the idle task is “chewing up 95 percent of the processor’s cycles,” that’s normal: it simply means your CPU isn’t working very hard on anything at the moment.